[新しいコレクション] yield strength 176512-Yield strength equation
The yield point R e (yield strength) is a material characteristic value and is determined using tensile testing (eg standard series ISO 62 (for metallic materials) or standard series ISO 527 (for plastics and composites)) The yield point is specified in MPa (megapascal) or N/mm² Often an upper yield point R eH and a lower yield point R eL can be determinedThe yield strength of a bolt can be defined as the tensile force that will produce a certain amount of permanent deformation within a specific fastener In many (but not all) bolting situations, it's important not to tension a bolt past its yield strength, because it no longer retains its original size and shape and ultimately its performanceThe yield strength or yield point of the material is defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically Prior to the yield point the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Ultimate Strength

Yield Strength Engineer Educators Com
Yield strength equation
Yield strength equation-Search en wood timber mechanical properties fible stress density elasticity ;Yield Strength The maximum load at which a material exhibits a specific permanent deformation Proof Load An axial tensile load which the product must withstand without evidence of any permanent set 1MPa = 1N/mm 2 = 145 pounds/inch 2 Shop for US Bolts Shop for Metric Bolts


Difference Between Yield Strength And Tensile Strength
The main difference between yield strength and tensile strength is that yield strength is the minimum stress under which a material deforms permanently, whereas tensile strength describes the maximum stress that a material can handle before breaking Stress – Strain Characteristics of a MaterialStrength, ductility and toughness are three very important, closely related material properties The yield and ultimate strengths tell us how much stress a mYield strength σ y Yield strength is defined in engineering as the amount of stress (Yield point) that a material can undergo before moving from elastic deformation into plastic deformation Yielding a material deforms permanently;
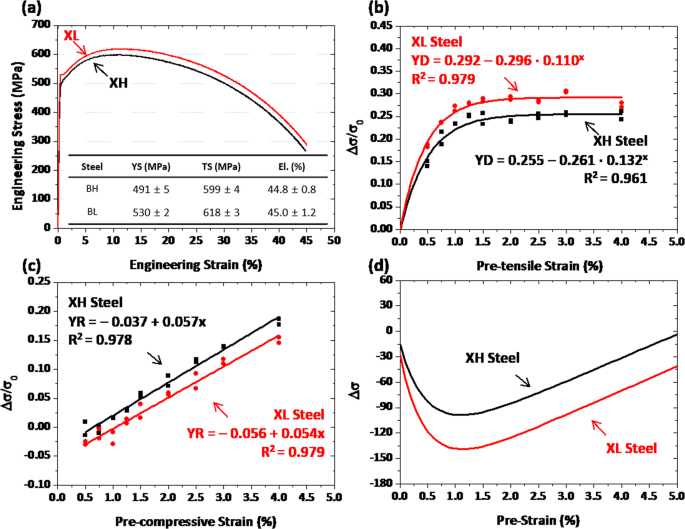
The yield strength of the sample at the various cooling rates Both methods show that as the cooling rate of the metal decreases the yield strength also decreases Introduction The average size of the grains in a given metal sample is a critical value Using the HallPetch equation the grain size can be used to determine the yield strength of aYield strength is the term used to refer to an indication of the maximum stress that can be developed in a substance without causing it to plastically deform Yield strength is the stress point at which a material becomes permanently deformed, providing a useful approximation of that material's elastic limitYield strength is the maximum stress that can be applied before it begins to change shape permanently This is an approximation of the elastic limit of the steel If stress is added to the metal but does not reach the yield point, it will return to its original shape after the stress is removed When the stresses exceed the yield point, the
Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress isThe yield strength of a material represents the stress beyond which its deformation is plastic Any deformation that occurs as a result of stress higher than the yield strength is permanent Because of the linearity of elastic deformation, yield strength is also defined as the greatest stress achievable without any deviation from theThe yield strength is the point where dislocation motion is easier than atomic bond stretching So, to increase the yield strength you can increase the strength of the atomic bonds (not really possible without completely changing the material), or you can make dislocation motion more difficult


What Is The Basic Difference Between Yield Strength And Ultimate Strength For Any Elastic Material Quora



Stress Strain Curve How To Read The Graph
The yield strength or yield stress is a material property and is the stress corresponding to the yield point at which the material begins to deform plastically The yield strength is often used to determine the maximum allowable load in a mechanical component, since it represents the upper limit to forces that can be applied without producingYield strength Stress level, measured at room temperature, at which material plastically deforms and does not return to its original dimensions when the load is released NOTE All yield strengths specified in this document are the 0,2 % offset yield strength in accordance with ISO 621 or ASTM A370EN steel grade specification is a high yield strength structural steels in the quenched and tempered condition steel plate grade in S500QL, S500QL1, S460Q, S460QL, S460QL1, S6QL1, S550Q, S550QL, S550QL1, S500Q, S0QL1, S960Q, S960QL, S6Q, S6QL, S690Q, S690QL, S690QL1, S0Q and S0QL steel plate grade



Shows The Values Of Ultimate Tensile Strength Uts And Values Of Yield Download Scientific Diagram



Strength At Break Tensile
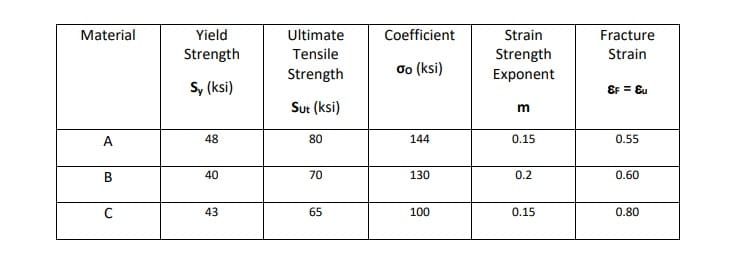
The stressstrain diagram for a steel rod is shown and can be described by the equation ε=0(1e06)σ0(1e12)σ 3 where s in kPa Determine the yield strength assuming a 05% offsetYield Strength is the stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation or a point at which it will no longer return to its original dimensions (by 02% in length) Whereas, Tensile Strength is the maximum stress (usually represented in PSI) that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before failing or breakingYield strength is mainly used there Another criterion might be based on the instances found in a google search "Yield strength" produces results, "yield stress" produces results


Properties Of Metals Engineering Library


Yield Strength Prediction Of Flattened Steel Pipes By Competing Bauschinger Effect And Strain Hardening During Pipe Forming Scientific Reports
Whether an object is stubborn or malleable is decided by the yield strength It is the point at which an object ceases to be elastic and becomes plastic Yield strength helps us choose appropriate materials for the construction based on the requirementThe Yield Point is in mild or mediumcarbon steel the stress at which a marked increase in deformationThe yield strength of a bolt can be defined as the tensile force that will produce a certain amount of permanent deformation within a specific fastener In many (but not all) bolting situations, it's important not to tension a bolt past its yield strength, because it no longer retains its original size and shape and ultimately its performance



Yield Strength Versus Ultimate Strength Physics Stack Exchange



How To Find Yield Strength Quora
Yield strength is the stress at which a material has undergone some arbitrarily chosen amount of permanent deformation, often 02 percent A few materials start to yield, or flow plastically, at a fairly welldefined stress (upper yield point) that falls rapidlyThe yield strength is defined as the stress at which a predetermined amount of permanent deformation occurs When subjected to stress, a material undergoes deformation, yield strength describes the maximum amount of stress required to elastically deform the material in a given loading arrangement like tension and compressionWhether an object is stubborn or malleable is decided by the yield strength It is the point at which an object ceases to be elastic and becomes plastic Yield strength helps us choose appropriate materials for the construction based on the requirement



Structural Steel Shapes Are Available In The Us With Different Yield Strength Fy And Ultimate Strength Fu As Established By Astm L Shape Steel Things To Know


Difference Between Yield Strength And Tensile Strength
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS) is considered as the failure criteria for brittle material In ductile materials, yield strength is much lower than ultimate strength For ductile materials, ultimate strength is roughly 15 times higher than yield strength Yield strength is used while designing components or structures made of ductile materialsYield Strength vs Tensile Strength Yield Strength is the stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation or a point at which it will no longer return to its original dimensions (by 02% in length) Whereas, Tensile Strength is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before failing or breakingYoung's Modulus Tensile and Yield Strength for common Materials Young's Modulus or Tensile Modulus alt Modulus of Elasticity and Ultimate Tensile and Yield Strength for steel, glass, wood and other common materials;


What Is Yield In Materials Yield Stress Yield Strength And Yield Point Materials Science Engineering



Offset Yield Strength Instron
In a previous post, we looked at the stressstrain curve and its relationship to various aspects of material strength — tensile strength, yield strength, and fracture strength, for example And while we often think of materials and structures in terms of strength, technically, "strength" is a measure of how much force a material can withstand before permanent deformation or failure occursUnderstanding the actual yield strength of a metal is just half the story The other half are the engineers who determine the required yield strength needed for steel, depending on the purposes for which it's being used This is the minimum yield strength needed for a projectYield strength is defined in engineering as the amount of stress (Yield point) that a material can undergo before moving from elastic deformation into plastic deformation Yielding – a material deforms permanently The Yield Point is in mild or mediumcarbon steel the stress at which a marked increase in deformation occurs without increase in


Material Coefficient Yield Strength Ultimate Tensi Chegg Com



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv
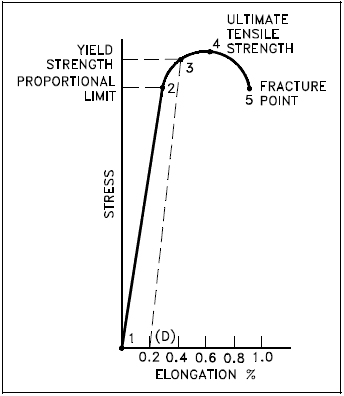
Yield Strength The yield point, or yield strength is the point on a stress–strain curve where elastic behavior ends and plastic behavior begins A more simplified definition is that Yielding means the start of breaking of fibers on the sample being testedStrength, ductility and toughness are three very important, closely related material properties The yield and ultimate strengths tell us how much stress a mYield Strength Definition Stress Strain Graph Stress Strain Graph Explanation Yield Strength Graph What is Yield Strength?



Yield Strength Engineer Educators Com



Mechanical Properties Of Materials Fractory
Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress isYield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress isYield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is


The Abc S Of Arc Welding Education Center Kobelco Kobe Steel Ltd



Yield Strength R Sub El Sub N Mm Sup 2 Sup Bossard Group
Yield Strength Definition Stress Strain Graph Stress Strain Graph Explanation Yield Strength Graph What is Yield Strength?Tensile / yield strengths and ductilities for some of the plain carbon and low alloy steels are given in the following mechanical properties of steel chart Yield Strength, Tensile Strength and Ductility Values for Steels at Room TemperatureStrength / Mechanics of Materials A number of terms have been defined for the purpose of identifying the stress at which plastic deformation begins The value most commonly used for this purpose is the yield strength The yield strength is defined as the stress at which a predetermined amount of permanent deformation occurs The graphical



New Perspectives On The Grain Size Dependent Yield Strength Of Polycrystalline Metals Sciencedirect



Yield Strength For Boneheads Engineeringclicks
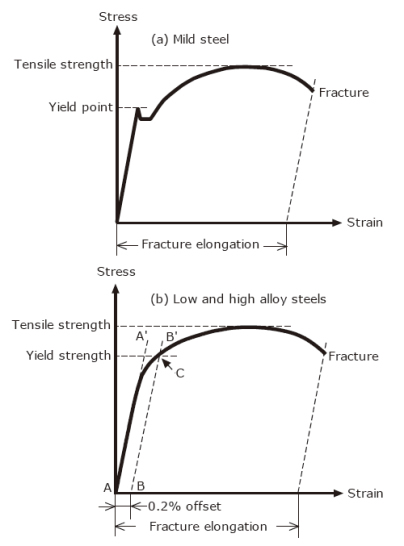
Yield Strength Testing The stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation This is not a sharply defined point Yield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Point at which material exceeds the elastic limit and will not return to its origin shape or length if the stress is removedYield Strength The maximum load at which a material exhibits a specific permanent deformation Proof Load An axial tensile load which the product must withstand without evidence of any permanent set 1MPa = 1N/mm 2 = 145 pounds/inch 2 Shop for US Bolts Shop for Metric BoltsUltimate tensile strength (UTS), often shortened to tensile strength (TS), ultimate strength, or within equations, is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking In brittle materials the ultimate tensile strength is close to the yield point, whereas in ductile materials the ultimate tensile strength can be higher



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv



Yield Engineering Wikipedia
EN steel grade specification is a high yield strength structural steels in the quenched and tempered condition steel plate grade in S500QL, S500QL1, S460Q, S460QL, S460QL1, S6QL1, S550Q, S550QL, S550QL1, S500Q, S0QL1, S960Q, S960QL, S6Q, S6QL, S690Q, S690QL, S690QL1, S0Q and S0QL steel plate gradeThe yield strength is a material constant that represents the limit of its elastic behavior Ductile materials like iron boast higher yield strength values than plastics, such as polyethylene Stresses so severe can cause permanent deformationsTensile strength, maximum load that a material can support without fracture when being stretched, divided by the original crosssectional are of the material Tensile strengths have dimensions of force per unit area, which are commonly expressed in units of pounds per square inch



Variations Of Initial Stress R I Voce With True Yield Strength R Y Download Scientific Diagram



Nominal Values Of The Yield Strength F Y And The Ultimate Tensile Download Table
Tensile strength, maximum load that a material can support without fracture when being stretched, divided by the original crosssectional are of the material Tensile strengths have dimensions of force per unit area, which are commonly expressed in units of pounds per square inchThe yield strength of the sample at the various cooling rates Both methods show that as the cooling rate of the metal decreases the yield strength also decreases Introduction The average size of the grains in a given metal sample is a critical value Using the HallPetch equation the grain size can be used to determine the yield strength of aYield strength is a measurement of how well a steel material can hold up to stress Through mathematical formulas and testing, metal professionals calculate the amount of stress that is necessary to cause the metal to deform In the case of steel, high yield steel will hold up to stress and pressure better than low yield steel



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet
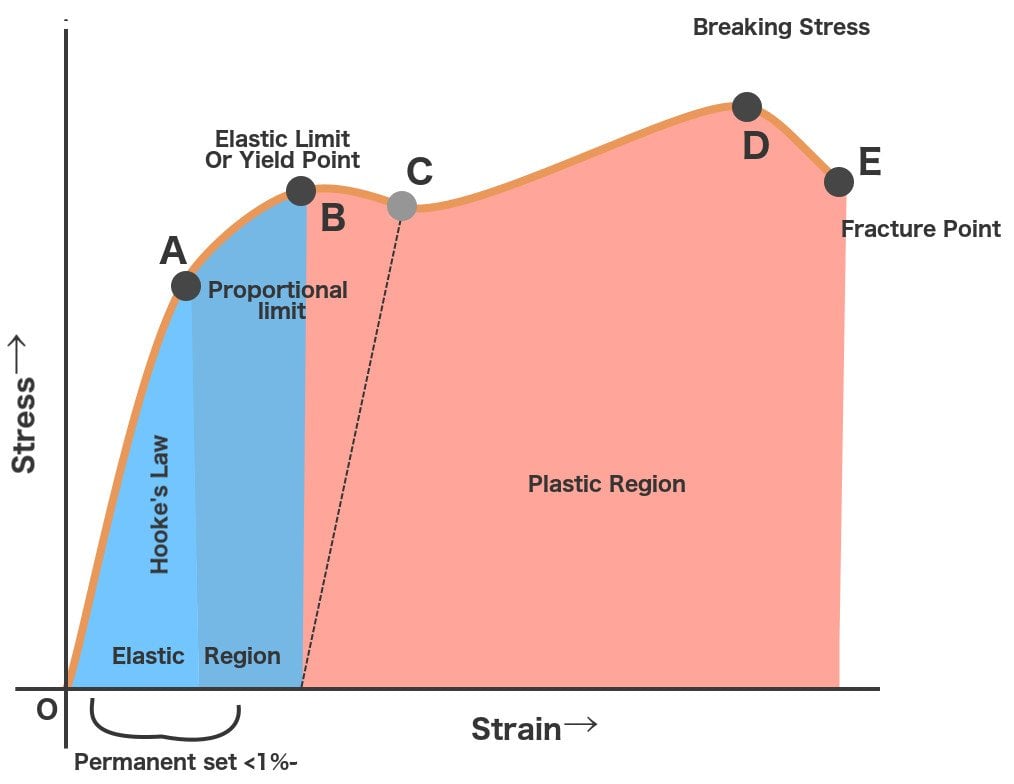


Yield Strength Defintion Examples And A Simplified Explanation
Yield strength is the amount of stress at which plastic deformation becomes noticeable and significant Fig1 is an engineering stressstrain diagram in tensile test Because there is no definite point on the curve where elastic strain ends and plastic strain begins, the yield strength is chosen to be that strength when a definite amount ofYield strength is the stress at which a material has undergone some arbitrarily chosen amount of permanent deformation, often 02 percent A few materials start to yield, or flow plastically, at a fairly welldefined stress (upper yield point) that falls rapidlyMechanical spring motion has been positioned to apply via way of means of human beings because the invention of crossbow Although theoretical knowhow of yield



How Come The Yield Strength Is Greater Than Tensile Strength When Testing A Steel Specimen Quora


Tensile Testing
Offset yield strength is an arbitrary approximation of a material's elastic limitIt is the stress that corresponds to a point at the intersection of a stressstrain curve and a line which is parallel to a specified modulus of elasticity line This parallel line is horizontally offset by a predetermined amount



Isbt212 04 3 Stress And Strain Proportional Limit And Yield Strength Youtube



Shear Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
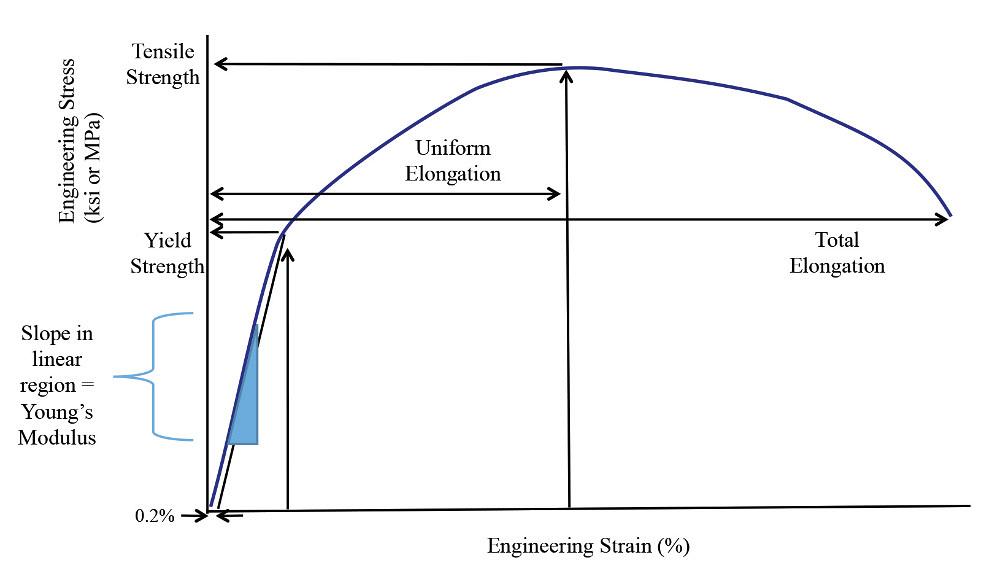


Getting To Know More About The Metal You Are Forming



Fastener Ultimate Tensile Strength Vs Yield Strength Which Is More Important Extreme Bolt



What Is The Relation Between Tensile Strength And Young S Modulus Of A Material



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve



Tensile Strength Of Steel Vs Yield Strength Of Steel Clifton Steel



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet



Yield Strength F Y Of Structural Steel S355j2h Test Results With Download Scientific Diagram
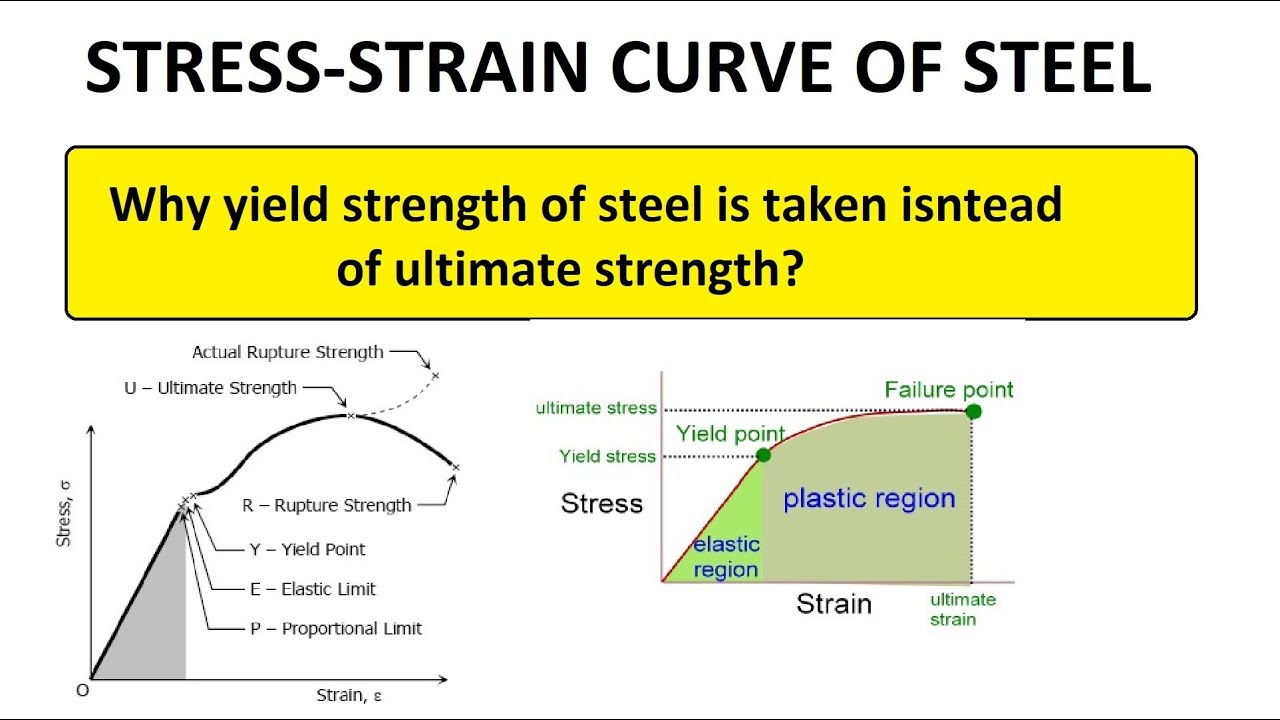


Hindi Stress Strain Curve For Steel Yield Strength Vs Ultimate Strength Youtube



How To Determine The Yield Strength Of Brass Quora



Bending Machines Should I Use Yield Point Or Tensile Strength Quora



What Is The Von Mises Stress And The Yield Criterion


Finding 0 2 Offset Strain Dplot
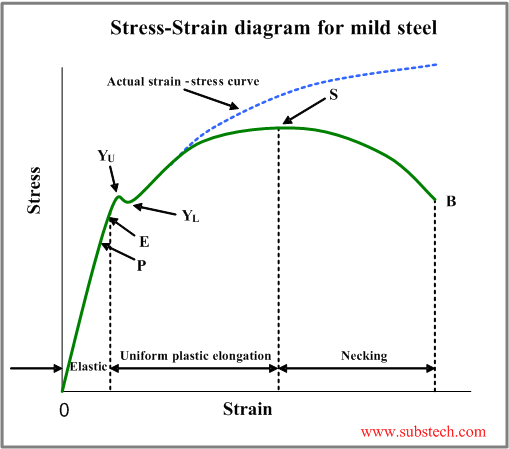


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech
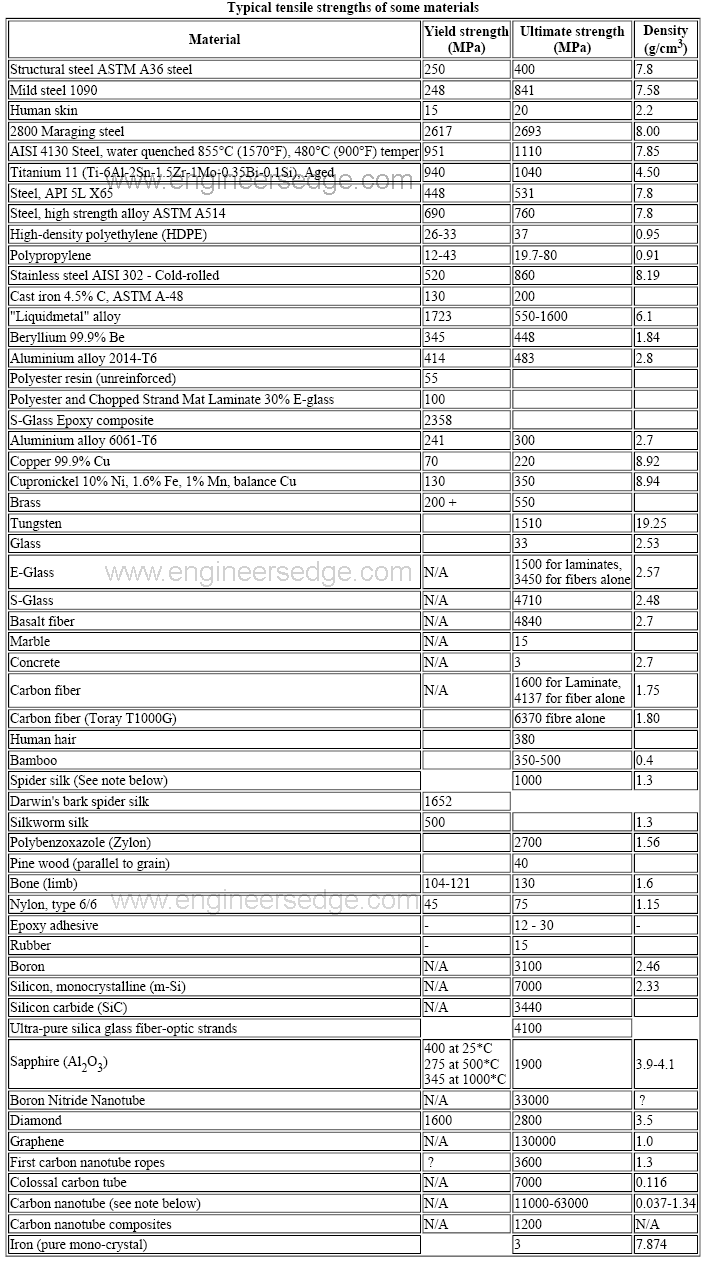


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



How To Find Yield Strain Corresponding To 0 2 Offset Yield Stress



Allowable Stress In Asme Viii 1 3 Api 650 Api 653 Amarine



Sheet Metal Tension Testing Admet



Yield Strength Metallurgy For Dummies


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs


Q Tbn And9gcq6zmctjndkkjpyak Xrcdf5heom0h Yhbhe5u3bt9reft0h3if Usqp Cau


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau



Yield Stress Of A Material Simple Explanation Civildigital
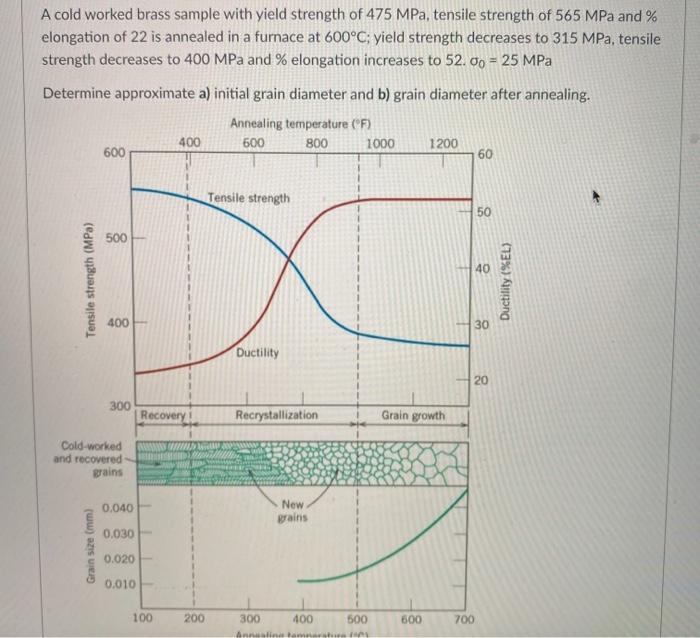


Solved A Cold Worked Brass Sample With Yield Strength Of Chegg Com
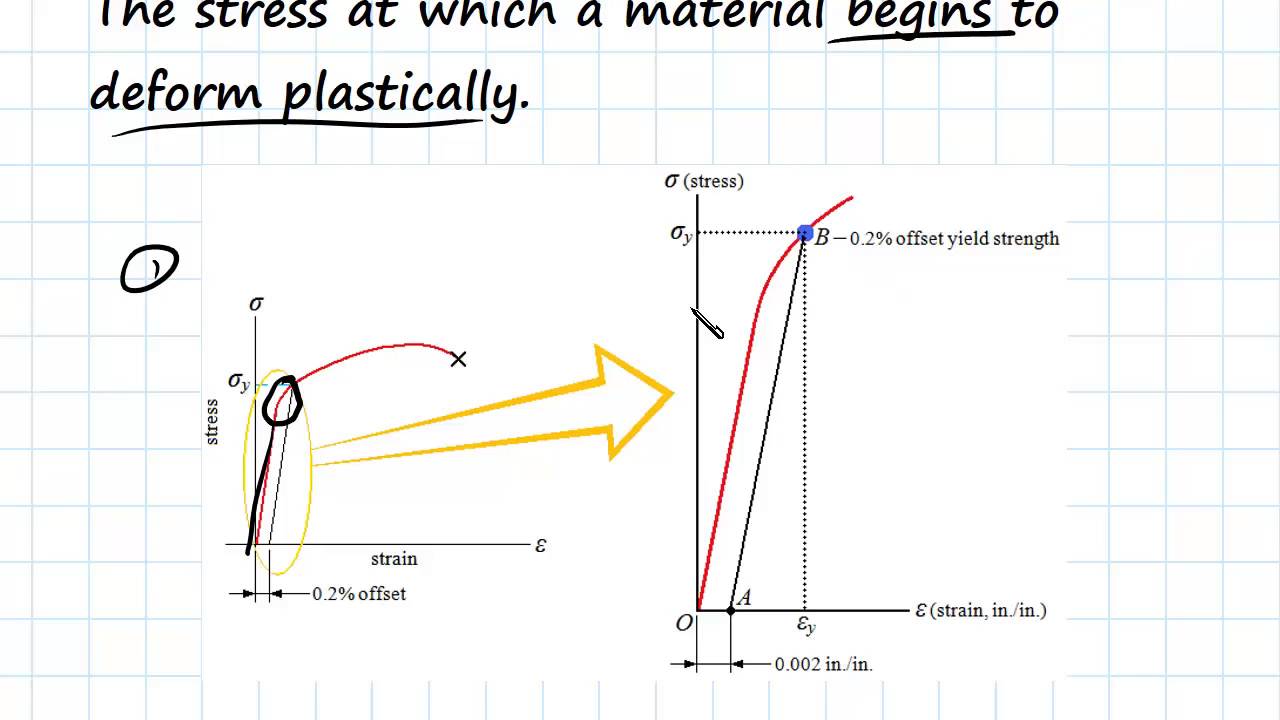


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube


Q Tbn And9gctk9iq8odyr8oad6ztec3f7a2cfwevlxhbui8zaefsdyzdh0s1n Usqp Cau



Tensile Strength Of Steel Vs Yield Strength Of Steel Clifton Steel


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau



Estimating Tensile Strength From Yield Or 0 2 Proof Values Twi
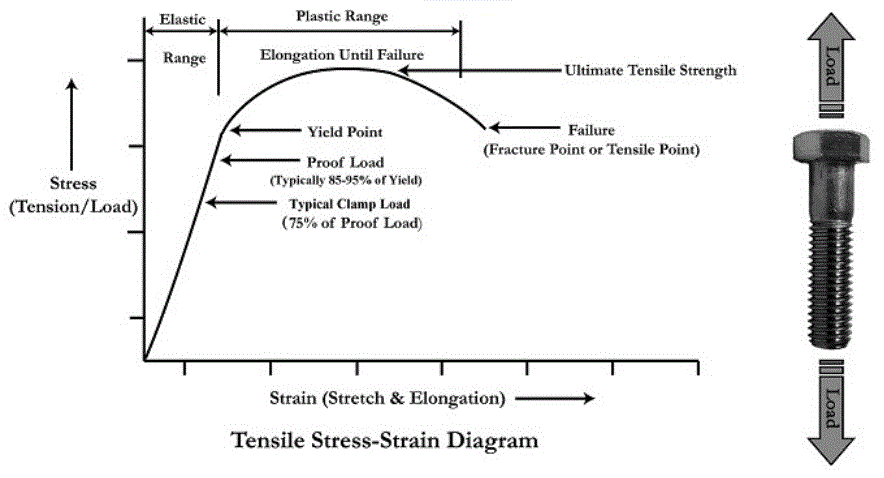


Thread Yield And Tensile Strength Equation And Calculator Engineers Edge Www Engineersedge Com
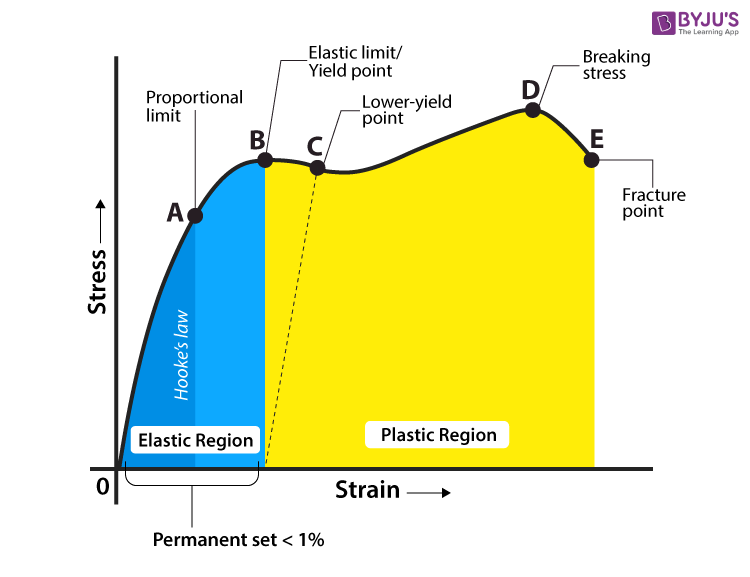


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



Yield Strength Vs Tensile Strength What Is The Difference Diffzi
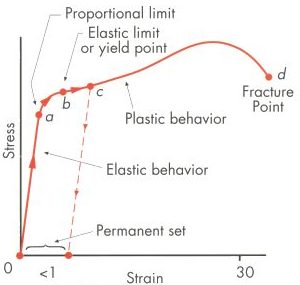


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
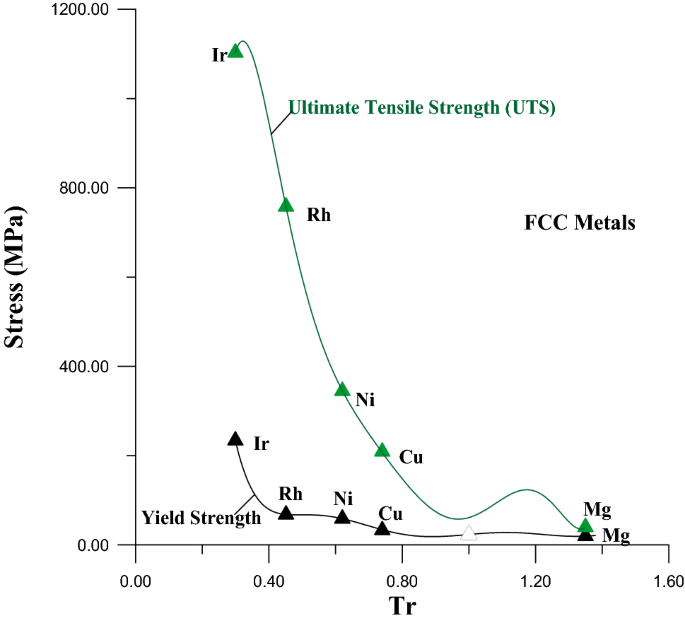


Estimation Of The Ultimate Tensile Strength And Yield Strength For The Pure Metals And Alloys By Using The Acoustic Wave Properties Scientific Reports


What Is The Ultimate Tensile Strength And Yield Strength Of Mild Steel And Hysd Bar Quora



Yield Strength And Hardness
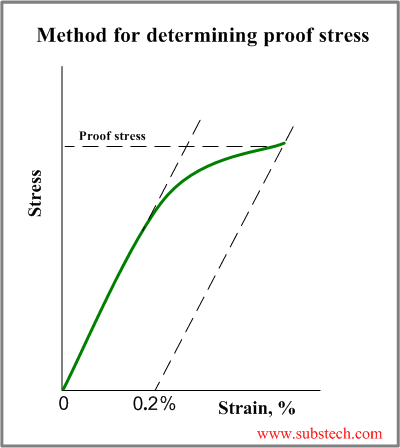


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech
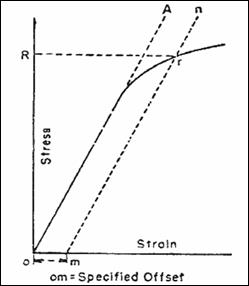


To Determine Yield Strength Tensile Strength Of A Steel Bar By Offset Secant Method
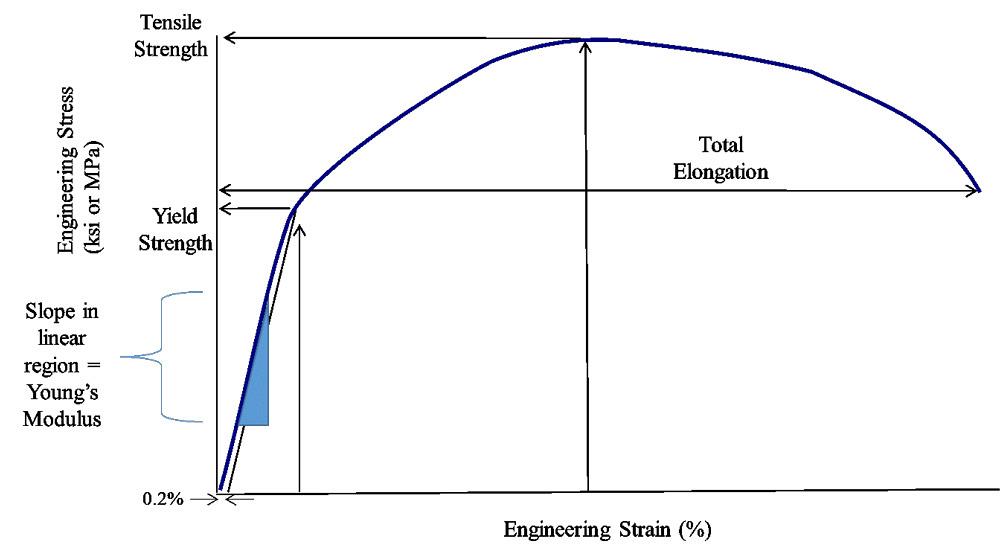


The Differences Between Stiffness And Strength In Metal


What Is The Difference Between Tensile And Yield Strength Quora
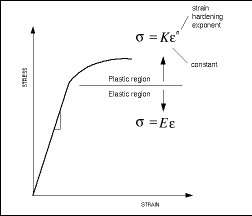


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers


9 Yield Stress Glass Phase Viscoelasticity



Yield Strength
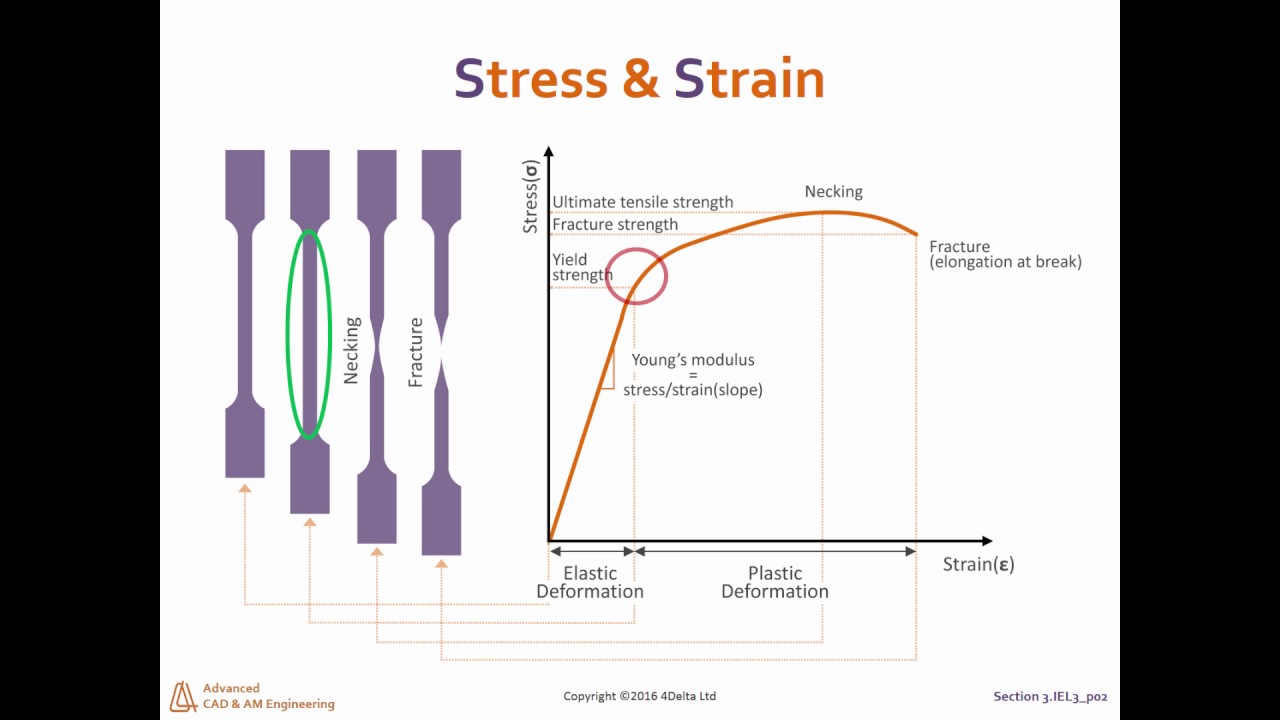


Yield Stress Yield Strenght Youtube



Motion Design 101 Stress Strain Curves Machine Design
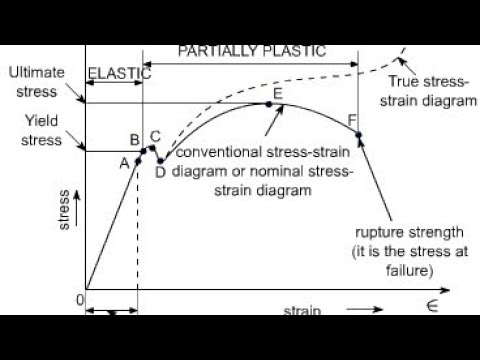


Stress Vs Strain Curve Yield Point Yield Strength Elastic Limit Neking Ultimate Tensile Youtube



Yield Strength Tensile Strength Elongation Hardness Of Sts304 In Download Table
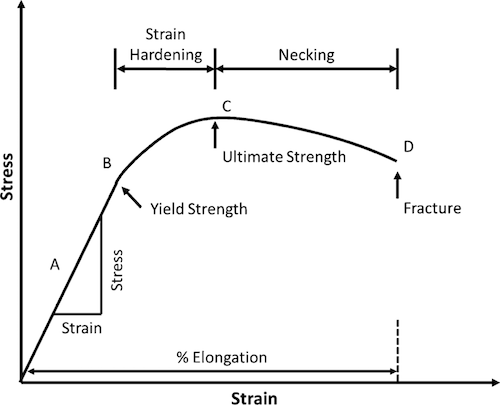


Cee 3710 Strength Versus Stiffness


Engarc L Offset Yield Method
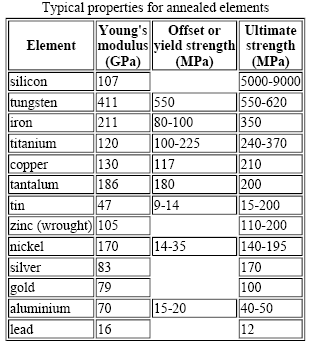


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Stress Strain Diagrams Showing Methods Of Yield Strength Determination Download Scientific Diagram



Pdf Yield Strength Estimation For Stainless Steel Using Plane Strain Compression Test Semantic Scholar
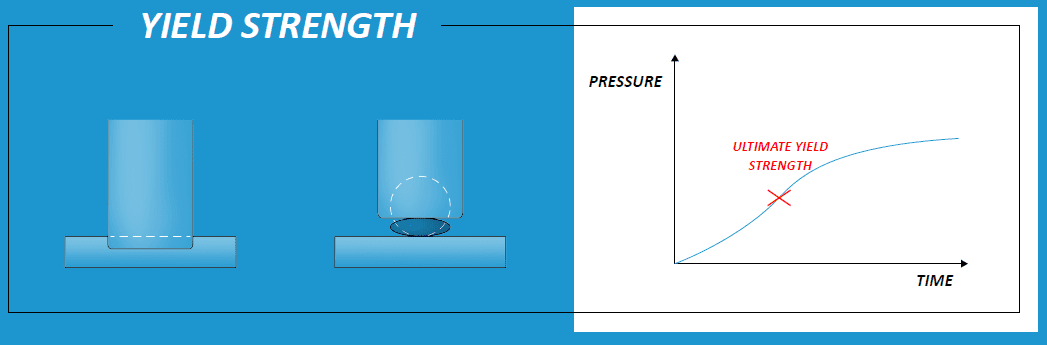


Instrumented Indentation Ultimate Yield Strength And Fatigue Nanoveananovea



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



What Is The Difference Between 0 2 Yield Stress And Yield Stress In Aluminum Quora
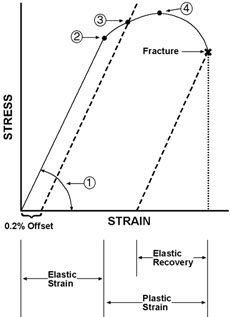


Industrial Design Guide Yield Strength



Proof Load Yield Strength And Tensile Strength Wilson Garner Company



Does Unloading Beyond Yield Point Also Affect Tensile Strength Engineering Stack Exchange
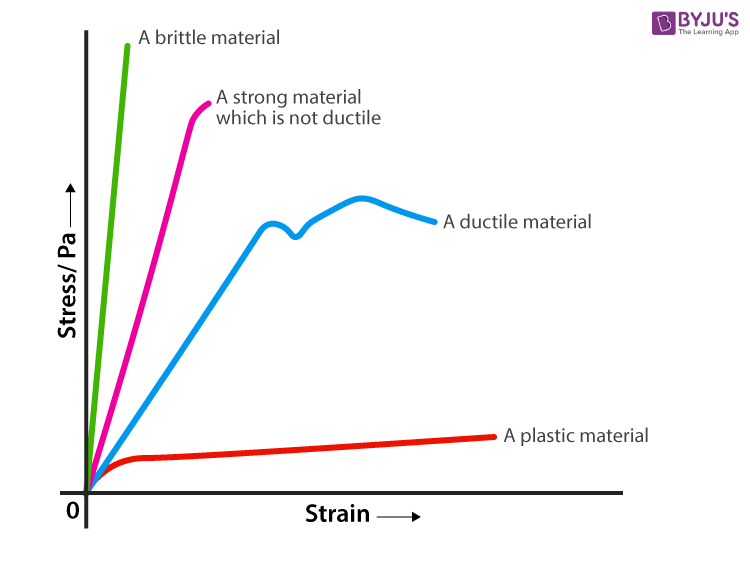


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
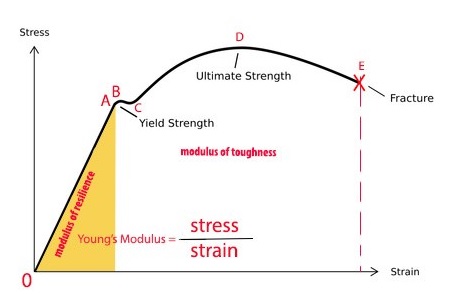


Exploring The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel The Chicago Curve



What Is Yield In Materials Yield Stress Yield Strength And Yield Point Materials Science Engineering



Range Of Yield Strength And Tensile Strength Of Tensile Tests Run At Download Scientific Diagram



Yield Point Instron


What Is The Difference Between The Yield Strength Re And The Practical Limit Rp Of A Material Quora



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve



Yield Strength In Exhaust Tubing Aluminum Vs Stainless Steel Burns Stainless



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
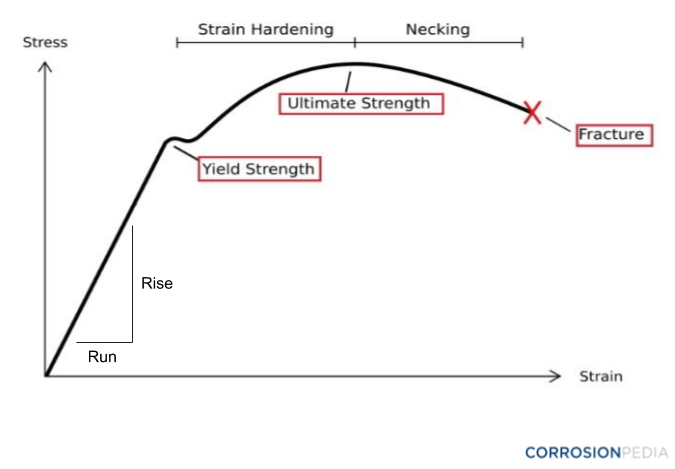


What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia
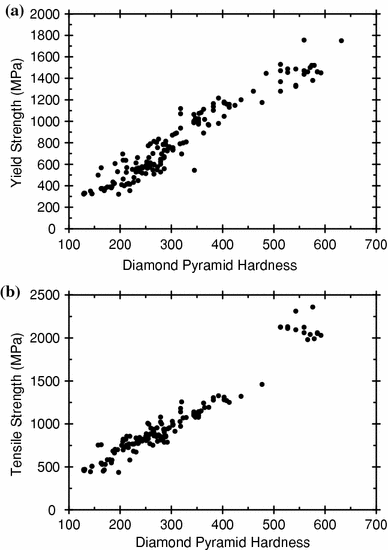


Correlation Of Yield Strength And Tensile Strength With Hardness For Steels Springerlink



Definition Of Yield Point Download Scientific Diagram
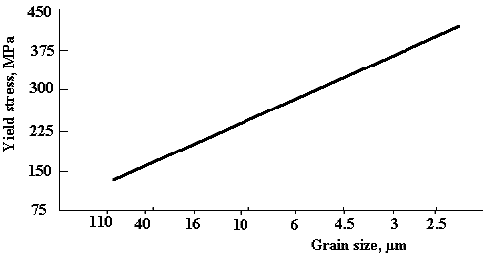


Yield Strength Testing Yield Strength Ultimate Strength Breaking Strength
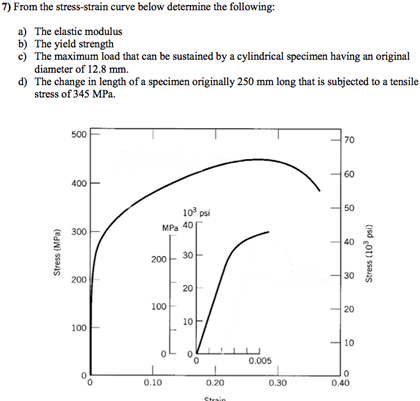


Solved From The Stress Strain Curve Below Determine The F Chegg Com


コメント
コメントを投稿